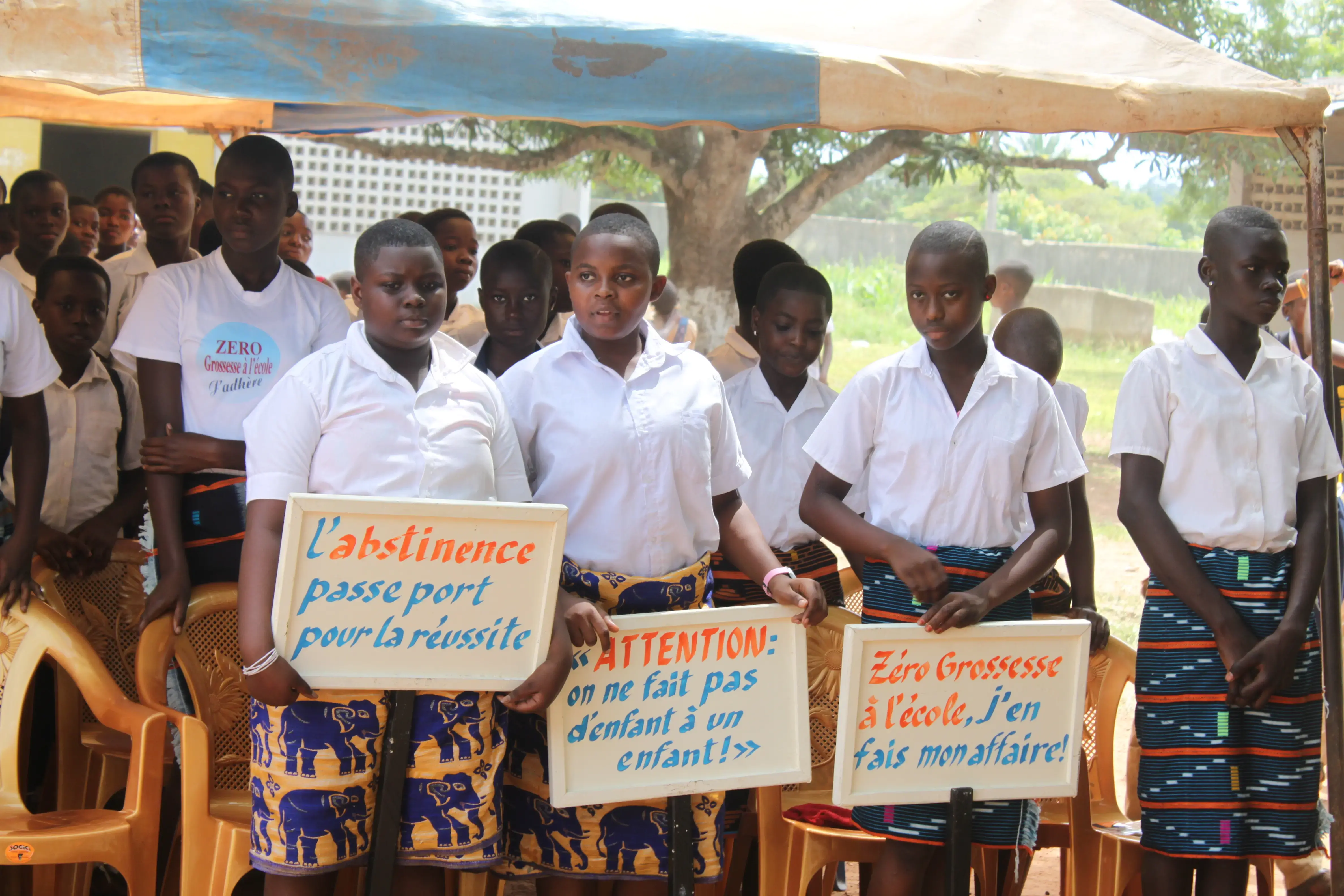
Eighty per cent of unintended pregnancies among adolescents occur among those who do not use modern contraception or rely on traditional methods. Compared to other age groups, adolescents who are married or in a union have the lowest use of contraception and the highest levels of unmet need.
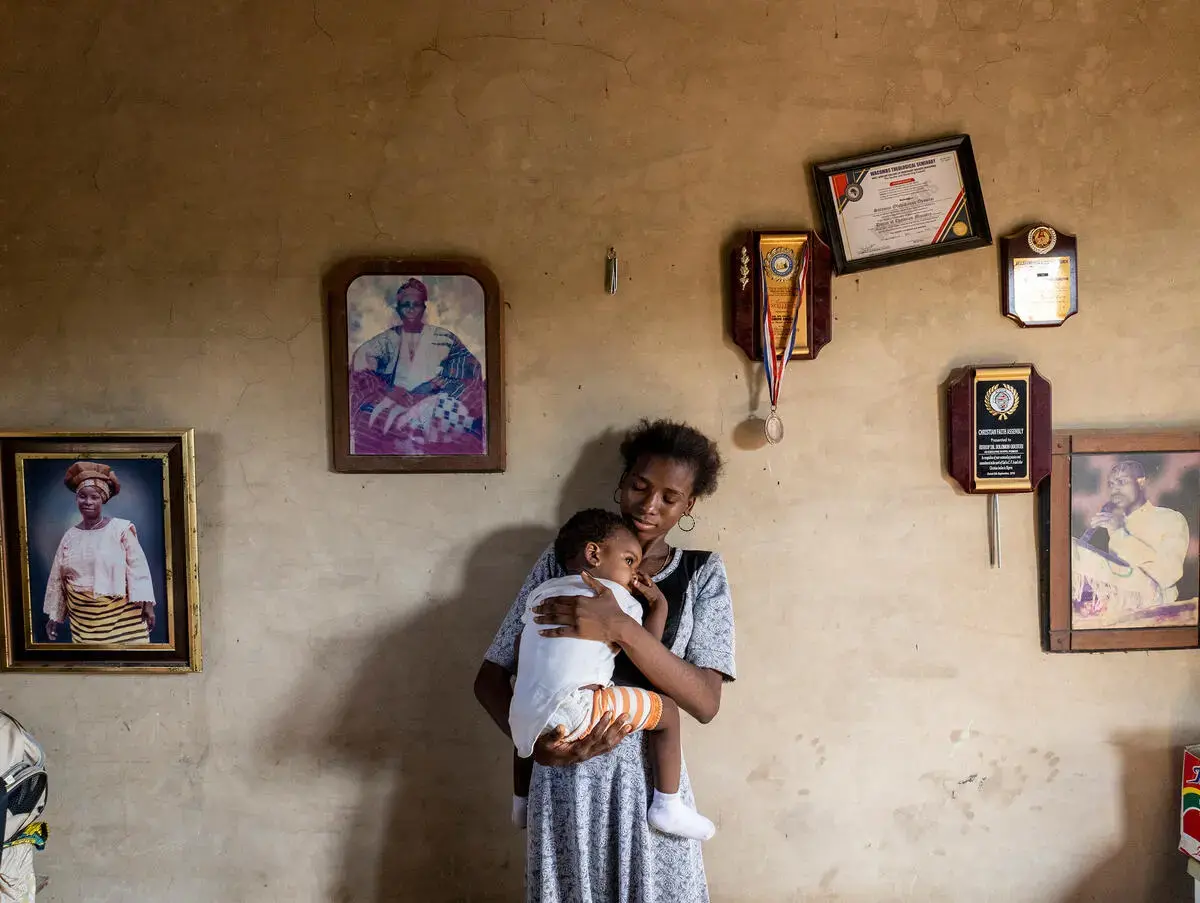
Complications from pregnancy and childbirth are a leading cause of death in adolescent girls and young mothers are more at risk of suffering obstetric fistula.
West and Central Africa has the largest percentage (6%) of reported births before age 15.
During and immediately following the civil war, teenage pregnancy and sexual violence spiked in Cote d’Ivoire; and the context is similar in Central African Republic and around the Lake Chad Basin.
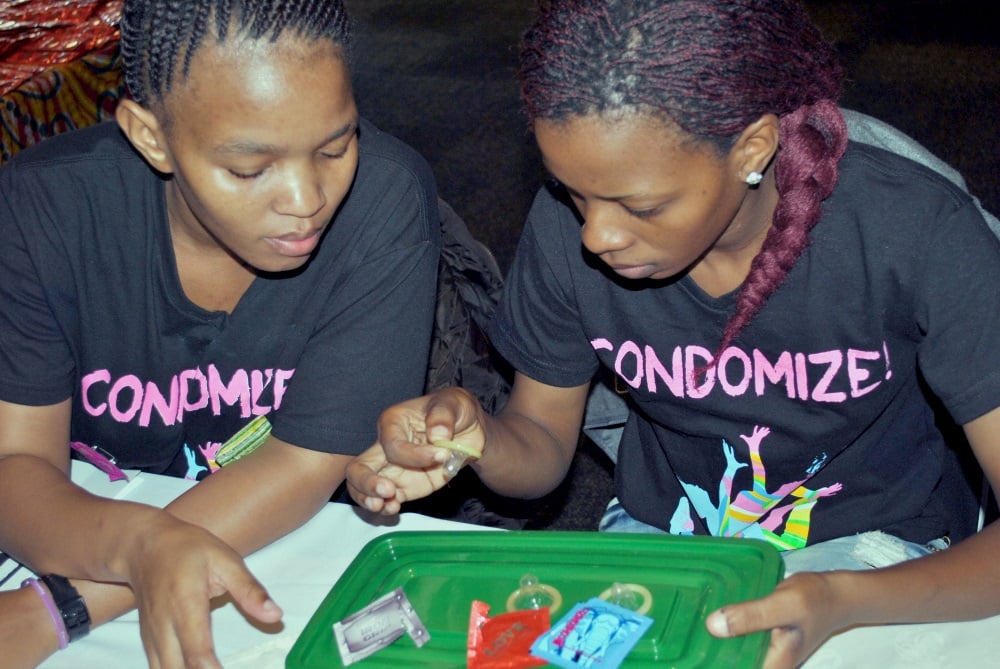

UNFPA-supported initiatives are helping to bend the curve and ensure more girls survive and thrive and avoid pregnancy. UNFPA also advocates supporting girls who become pregnant so they can return to school and reach their full potential.